Table of Contents

Best alcohol to drink with uti
When it comes to the best alcohol to drink with uti, it’s important to prioritize your health and recovery. Alcohol is known to be a diuretic, which means it increases urine production. In the case of a UTI, it’s generally advisable to stay hydrated and avoid substances that can irritate the bladder or worsen the infection.
Drinking plenty of water is usually recommended to flush out bacteria and help alleviate UTI symptoms. It’s important to listen to your body and give it the care it needs. If you’re looking for a comforting beverage, you could try herbal teas like chamomile or cranberry juice (unsweetened) that may help support urinary health. However, it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice, as they can provide specific guidance based on your condition and medical history.
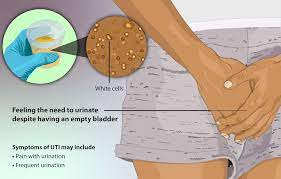
What Does A Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
UTIs are quite common and can happen when bacteria, usually from the digestive tract, enter the urinary system. The urinary system consists of your kidneys, bladder, ureters (tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder), and urethra (the tube through which urine passes out of your body).
UTIs often occur when bacteria, such as E. coli, make their way up the urethra and into the bladder. This can happen due to various factors like improper wiping after using the bathroom, sexual activity, or using irritating products in the genital area. Women tend to be more prone to UTIs because their urethra is shorter, making it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder.
What are the symptoms of a UTI?
Certainly! I’d be happy to discuss the symptoms of a urinary tract infection (UTI) with you. UTIs can cause a range of uncomfortable symptoms. Here are some common signs to look out for. It’s important to remember that symptoms can vary from person to person, and some individuals may not experience all of these symptoms, such as fever, back pain, or nausea.
- Frequent urge to urinate: You may find yourself needing to urinate more often than usual. Even if you just went to the bathroom, you may feel the need to go again.
- Burning sensation or pain during urination: When you have a UTI, you might experience a burning or stinging sensation while passing urine. It can be quite uncomfortable.
- Cloudy or bloody urine: Your urine might appear cloudy, dark, or even have a reddish tinge due to the presence of blood. However, it’s important to note that not all UTIs result in bloody urine.
- Strong-smelling urine: If you notice a strong or unpleasant odor when you urinate, it could be a sign of a UTI. The odor is often different from your usual urine scent.
- Lower abdominal pain or discomfort: Some people with UTIs experience pain or a dull ache in the lower abdomen, which can range from mild to more intense discomfort.
What Are the Causes of a UTI?
UTIs are typically caused by bacteria entering the urinary system and multiplying, leading to an infection. The most common culprit is Escherichia coli (E. coli), a type of bacteria found in the digestive tract. However, other bacteria can also cause UTIs.Here are some common causes and risk factors for developing a UTI:
- Bacteria from the digestive tract: The most common cause of UTIs is when bacteria, like E. coli, make their way from the anus into the urethra and eventually reach the bladder. From there, they can travel further up the urinary tract and cause an infection.
- Sexual activity: Sexual intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urethra, increasing the risk of a UTI. This is why it’s often recommended to urinate before and after sexual activity to help flush out any potential bacteria.
- Female anatomy: Women have a shorter urethra compared to men, which means bacteria have a shorter distance to travel to reach the bladder. This anatomical difference makes women more prone to UTIs.
- Menopause: After menopause, the decline in estrogen levels can cause changes in the urinary tract, making it more susceptible to infections.
- Urinary tract abnormalities or blockages: Structural issues in the urinary tract, such as kidney stones or an enlarged prostate gland in men, can obstruct urine flow and increase the risk of UTIs.
- Catheter use: If you have a urinary catheter in place, it can introduce bacteria directly into the bladder, making UTIs more likely.
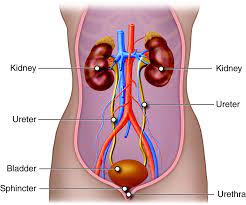
Infection of the Bladder
When we talk about an infection of the bladder, we’re usually referring to a condition called cystitis. Cystitis occurs when bacteria enter the bladder and cause an inflammation or infection.
The most common cause of bladder infections is bacteria, particularly Escherichia coli (E. coli) which normally resides in the digestive tract. Sometimes, these bacteria can travel from the urethra, the tube that carries urine out of the body, and reach the bladder. This can happen due to factors like improper wiping after using the bathroom or sexual activity.
The symptoms of a bladder infection can include a frequent urge to urinate, a burning or painful sensation during urination, cloudy or bloody urine, strong-smelling urine, and lower abdominal discomfort. However, it’s important to note that the severity and presentation of symptoms can vary from person to person.
Bladder infections are more common in women due to their shorter urethra, which allows bacteria to reach the bladder more easily. However, men can also develop bladder infections, which may be related to conditions like an enlarged prostate or catheter use.
If you suspect you have a bladder infection, it’s important to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can diagnose a bladder infection through a urine sample test and prescribe appropriate antibiotics to treat the infection.
In addition to medication, there are some steps you can take to help alleviate symptoms and prevent future bladder infections. Drinking plenty of water, urinating regularly, and practicing good hygiene (such as wiping front to back) can be helpful. It’s also advisable to avoid irritants like caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods that can further irritate the bladder.
Infection of the Urethra
Infections of the urethra can be caused by various factors, including bacteria, viruses, or even certain sexually transmitted infections (STIs). The most common cause of urethritis is bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli), or sexually transmitted bacteria like Neisseria gonorrhoeae or Chlamydia trachomatis.
The symptoms of urethritis can vary depending on the underlying cause, but common signs include a burning or stinging sensation during urination, an increased frequency of urination, an urgent need to urinate, and in some cases, discharge from the urethra. It’s important to note that these symptoms can also overlap with those of a urinary tract infection (UTI).
If you suspect you have urethritis or are experiencing symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. They may perform tests, such as a urine sample or a swab of the urethra, to identify the cause of the infection.
Treatment for urethritis typically involves addressing the underlying cause. If the infection is bacterial, antibiotics are often prescribed to target the specific bacteria causing the infection. For STIs, appropriate treatment options will be recommended based on the specific infection.
In addition to medication, there are steps you can take to help manage symptoms and prevent future infections. Drinking plenty of water, avoiding irritants like harsh soaps or douches, and practicing safe sex by using barrier methods (such as condoms) can help reduce the risk of urethritis.
Treatment for uti
When it comes to treating a UTI, the primary approach is typically through antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare professional.
If you suspect you have a UTI or have been diagnosed with one, it’s important to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional will evaluate your symptoms and may ask for a urine sample to confirm the presence of bacteria. Based on the specific bacteria causing the infection and its susceptibility to certain antibiotics, they will prescribe the most appropriate medication for you.
It’s crucial to take the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if you start feeling better before completing the medication. This ensures that the infection is fully eradicated and reduces the risk of recurring or persistent infections. Make sure to follow your healthcare professional’s instructions regarding the dosage and duration of the antibiotic treatment.
Along with antibiotics, there are some steps you can take to help relieve symptoms and support your recovery:
Drink plenty of water: Staying hydrated can help flush out bacteria and promote healing. Aim to drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day.
Urinate frequently: Don’t hold in urine for long periods, as it can allow bacteria to multiply. Urinating when you feel the need helps flush out bacteria from the urinary tract.
Avoid irritants: Steer clear of potential bladder irritants like caffeine, alcohol, spicy foods, and carbonated drinks. These substances can worsen UTI symptoms.
Apply heat: Applying a warm compress or using a heating pad on your lower abdomen can help alleviate any discomfort or pain associated with the UTI.

Why You Shouldn’t Drink Alcohol When Taking Antibiotics
It’s often advised to avoid drinking alcohol when you’re on a course of antibiotics, and here’s why:
Firstly, both alcohol and antibiotics are processed by the liver. When you consume alcohol, it can interfere with the liver’s ability to metabolize medications, including antibiotics. This can potentially reduce the effectiveness of the antibiotics in fighting off the infection you’re trying to treat.
Secondly, combining alcohol and antibiotics can cause unpleasant side effects. It can intensify the common side effects of antibiotics, such as nausea, dizziness, and drowsiness. These effects can be quite uncomfortable and may even make you feel worse while you’re trying to recover.
Additionally, alcohol can dehydrate your body, and staying properly hydrated is important for supporting your immune system and helping your body heal. UTIs can already cause discomfort and irritation in the urinary tract, and alcohol’s dehydrating effects can exacerbate these symptoms.
It’s worth noting that the interaction between alcohol and antibiotics can vary depending on the specific antibiotic you’re taking. So, it’s always best to follow the instructions provided by your healthcare professional or read the medication label carefully. If you’re unsure about the compatibility of your antibiotic with alcohol, it’s best to consult your healthcare professional or pharmacist for guidance.
While it may be tempting to have a drink while you’re on antibiotics, it’s generally recommended to abstain from alcohol until you’ve completed the full course of medication. Prioritizing your health and giving your body the best chance to fight off the infection is key.
What Other Drinks Should Be Avoided While Experiencing A UTI?
Sure, let’s talk about other drinks to avoid when you’re experiencing a urinary tract infection (UTI). When dealing with a UTI, it’s generally a good idea to be mindful of your beverage choices to help alleviate symptoms and support the healing process. Here are a few drinks you may want to consider avoiding or consuming in moderation:
- Caffeinated beverages: Drinks like coffee, tea, energy drinks, and certain sodas contain caffeine, which can act as a diuretic and increase urine production. This may result in more frequent trips to the bathroom, which can be uncomfortable when you have a UTI.
- Alcohol: As we discussed earlier, alcohol can be problematic when taking antibiotics for a UTI due to its potential interaction with the medication. Additionally, alcohol can dehydrate your body, which is not ideal when you’re trying to support your urinary tract’s healing process.
- Citrus juices: While citrus fruits like oranges and grapefruits are generally considered healthy, the acidic nature of their juices can irritate the bladder and worsen UTI symptoms. It’s best to avoid or limit the intake of citrus juices like orange or grapefruit juice until your symptoms subside.
The best drinks for urine infection
When it comes to choosing the best drink for a urinary tract infection (UTI), the key is to focus on staying well-hydrated. Drinking plenty of fluids can help flush out bacteria from the urinary tract and support the healing process. Here are some drinks that can be beneficial for UTI:
- Water: Pure and simple, water is often the best choice for staying hydrated. It’s essential for maintaining overall health and can help dilute urine, making it less irritating to the urinary tract.
- Cranberry juice: Cranberry juice has long been associated with UTIs. While it may not directly treat the infection, some studies suggest that cranberry juice might help prevent bacteria from sticking to the bladder wall. Opt for pure cranberry juice without added sugars, as sugary drinks can potentially worsen UTI symptoms.
- Herbal teas: Non-caffeinated herbal teas, such as chamomile or peppermint tea, can be soothing and hydrating. Some herbal teas, like dandelion or nettle tea, are believed to have diuretic properties, which may help increase urine flow.
- Unsweetened coconut water: Coconut water is a natural source of electrolytes and can provide hydration. It’s important to choose unsweetened varieties to avoid unnecessary sugars.
- Plain unsweetened yogurt: While not a drink per se, plain unsweetened yogurt contains beneficial bacteria called probiotics. These can support a natural remedies may offer some benefits for urinary tract infections (UTIs), it’s important to note that they should not replace medical treatment or prescribed antibiotics. If you suspect you have a UTI, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. That being said, some natural substances have been studied for their potential antimicrobial properties. Here are a few examples:
- D-mannose: D-mannose is a type of sugar that can be found naturally in fruits like cranberries. It’s believed to prevent bacteria from adhering to the urinary tract walls, potentially helping to flush them out. However, it’s important to note that D-mannose is not a substitute for antibiotics in treating an active UTI.
- Cranberry: Cranberries and cranberry juice have been traditionally associated with UTIs. They contain compounds that may inhibit bacteria from sticking to the bladder walls. While cranberry products may have a preventative effect, their effectiveness in treating an active UTI is limited.
- Garlic: Garlic has been studied for its potent antimicrobial properties, including against bacteria that can cause UTIs. However, more research is needed to determine its specific effectiveness and dosage in treating UTIs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, choosing the right drinks when dealing with a urinary tract infection (UTI) can play a supportive role in your recovery. Staying well-hydrated is essential, as it helps flush out bacteria and supports the healing process. Water is generally the best choice for hydration.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this conversation is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice. Urinary tract infections (UTIs) can vary in severity, and it’s essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. The discussion about drinks for UTIs is based on general knowledge and should not replace personalized medical guidance. Every individual’s situation is unique, and treatment recommendations may vary. Always follow the advice of your healthcare professional and seek their guidance regarding your specific condition.